Management
machines now run on Debian 8
Common
Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) vulnerabilities fixes using the CVE List. CVE
helps because it provides a standardised identifier for a given vulnerability
or exposure. Knowing this common identifier allows you to quickly and
accurately access information about the problem across multiple information
sources that are compatible.
Upgraded to Python 3.6.4
For the API which has a
significant improvement in API Stability.
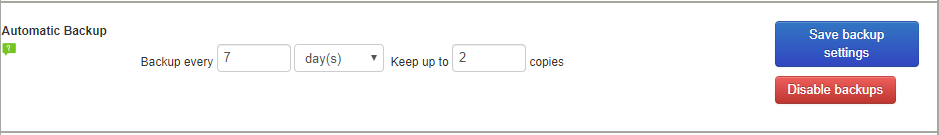
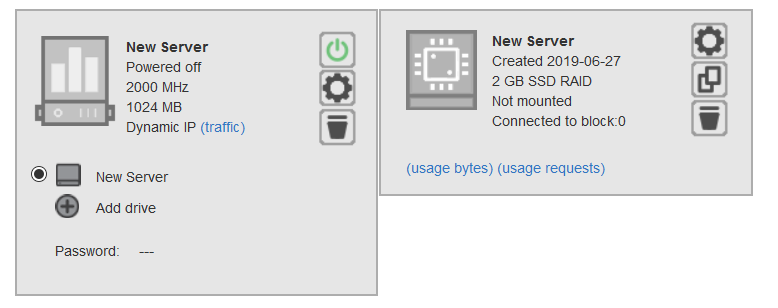
Automated Backups
In the drives and folder settings
page, users can now set automated backup policies (backup every X amount of days,
keep up to X amount of copies) and backups are taken (and old ones removed)
automatically.
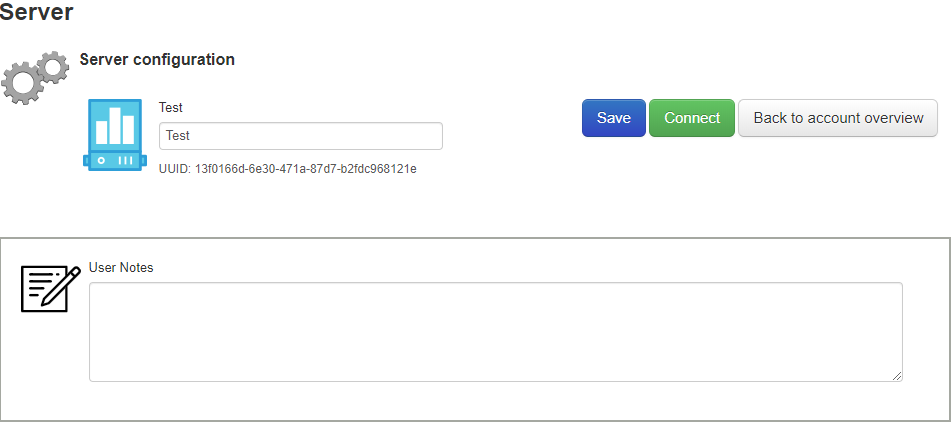
User Notes
Control panel support for user notes on virtualisation objects such as servers/drives/folders.
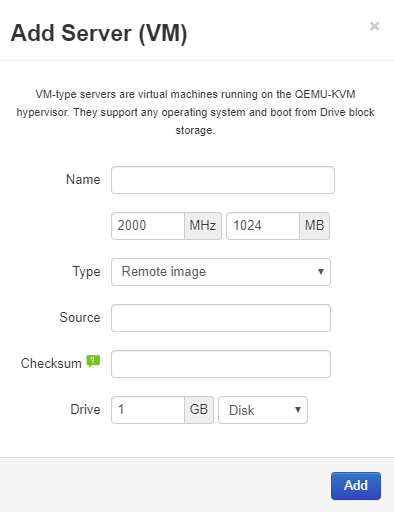
Remote Image Pulling
Drives can now be created by inputting the URL of an .iso file. The system will pull (and verify the checksum) of the image.
Microsoft Server 2016 is now
fully supported
Microsoft
is working closely with the Docker development team to bring Docker-based
containers to Windows Server. Until now, containers have existed almost
entirely in the Linux/UNIX open-source world. This allows you to isolate
applications and services in an agile, easy-to-administer way. Windows Server
2016 offers two different types of containerised Windows Server instances.
Secure
Boot is part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) specification
that protects a server’s start-up environment against the injection of rootkits
or other assorted boot-time malware.
- The Resilient File System
The
Resilient File System (ReFS) has been a long time coming in Windows Server. In
Windows Server 2016, we finally have a stable version. ReFS is intended as a
high-performance, high-resiliency file system intended for use with Storage
Spaces Direct (discussed next in this article) and Hyper-V workloads.
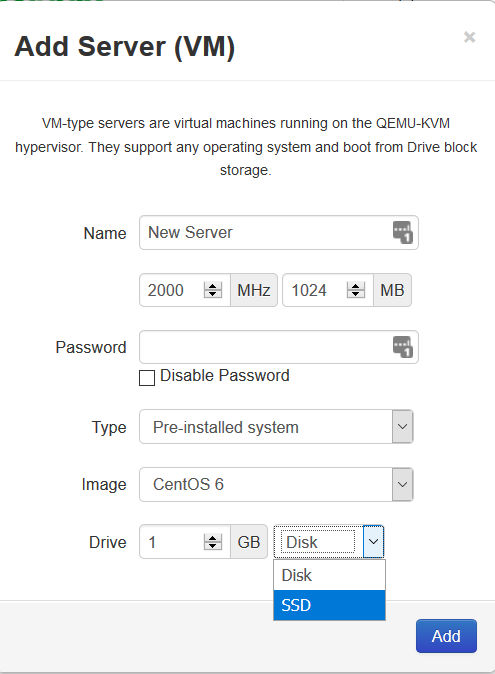
Solid State Drives
Available
on the management console.
- In
terms of read IOPS per watt, an SDD has up to an astonishing 179,500 percent
advantage over an HDD.
- SD can access memory addresses much
faster than the HDD can move drive heads. This dramatically higher performance
places SSD in the ideal position for high IOPs. Top performance storage tiers
frequently use only SSD, although a storage tier one step down may combine high
performance SSD with a high performing 15RPM HDD.
- SSDs are ideal for high performance
processing, whether they reside in an all-flash array or in hybrid storage
arrays. They clearly top HDD in performance. Companies typically reserve SSDs
for high performance applications.